4 Inch PVC Pipe: Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Specifications and Features
- Dimensions
- Material Composition
- Durability and Strength
- Applications and Uses
- Plumbing Systems
- Irrigation Systems
- HVAC and Ventilation Systems
- Installation and Maintenance
- Installation Process
- Maintenance Tips
- Advantages of PVC Pipes
- Cost Efficiency
- Corrosion Resistance
- Lightweight and Easy Handling
- Comparison with Other Pipe Materials
- PVC vs. Metal Pipes
- PVC vs. CPVC Pipes
- Safety and Compliance
- Safety Guidelines
- Regulatory Compliance
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
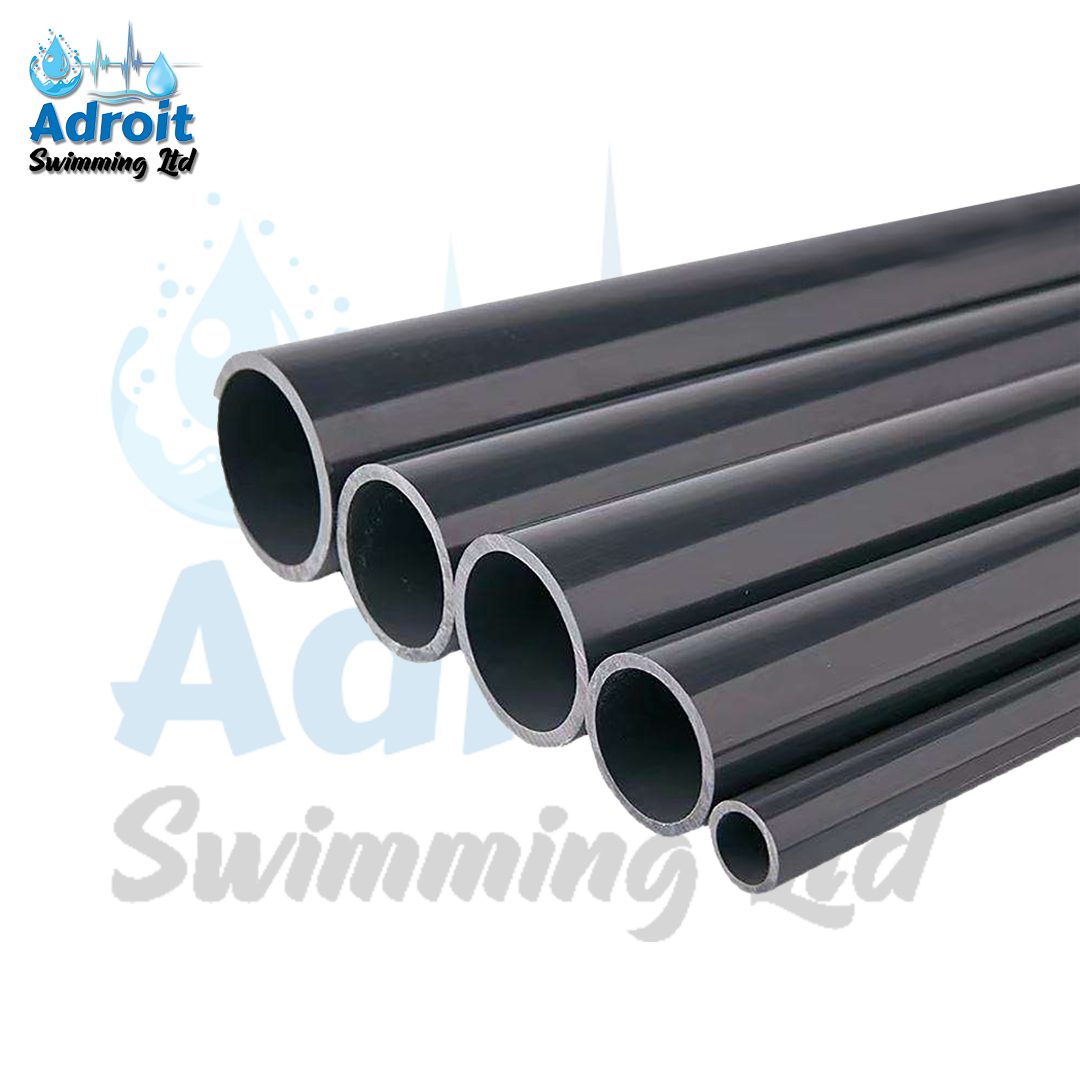
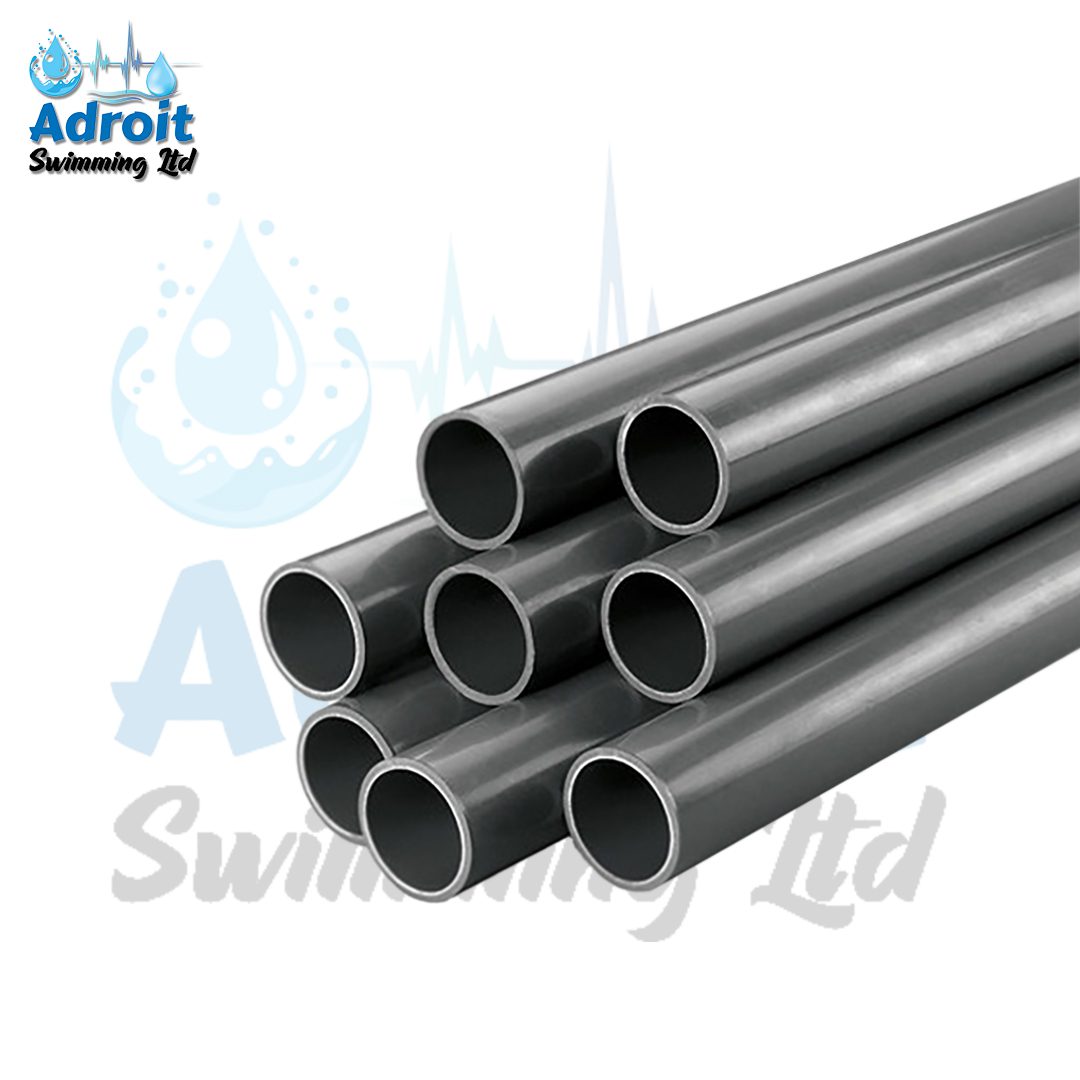
The 4-Inch PVC Pipe is a robust and versatile piping solution used extensively across various industries and applications. Constructed from high-quality Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), this pipe is designed to offer a reliable and efficient means of transporting fluids, gases, and other materials. With its substantial internal diameter and durable construction, the 4-inch PVC pipe is ideal for medium to large-scale installations, providing a combination of strength, resistance, and cost-effectiveness.
2. Specifications and Features
Dimensions
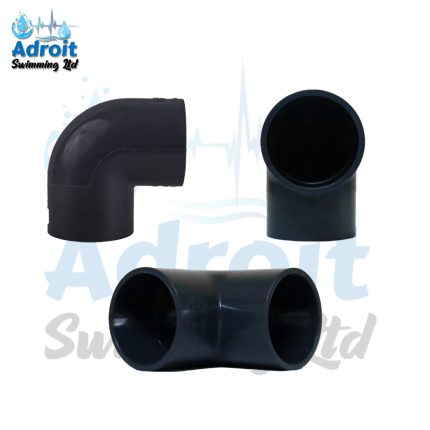
The 4-Inch PVC Pipe features an internal diameter of 4 inches, making it suitable for applications requiring a larger conduit for fluid or gas transport. The external diameter of the pipe is slightly larger to accommodate standard fittings and connectors. The nominal size of 4 inches refers to the pipe’s internal diameter, while the actual external diameter may vary slightly depending on the pipe’s schedule (e.g., Schedule 40 or Schedule 80) and wall thickness.
Material Composition
The 4-Inch PVC Pipe is manufactured from high-grade PVC, known for its beneficial properties such as rigidity, chemical resistance, and long-lasting durability. PVC, a thermoplastic polymer, maintains its structural integrity under a variety of environmental conditions. The pipe’s smooth interior ensures efficient fluid flow, while the exterior is designed to withstand physical impacts and environmental wear.
Durability and Strength
PVC pipes are well-regarded for their durability and resistance to corrosion, rust, and chemical degradation. The 4-Inch PVC Pipe is engineered to handle moderate to high pressures, depending on its schedule. This makes it suitable for a wide range of applications where strength and longevity are essential. The pipe’s resistance to environmental factors ensures reliable performance over time.
3. Applications and Uses
Plumbing Systems
In plumbing systems, the 4-Inch PVC Pipe is used for various applications, including water supply and drainage. Its robustness and resistance to corrosion make it suitable for residential, commercial, and industrial plumbing systems. The pipe can handle a variety of water flow conditions, ensuring efficient and reliable operation in plumbing networks.
Irrigation Systems
The 4-Inch PVC Pipe is extensively used in irrigation systems to distribute water from the source to different irrigation points. Its ability to withstand environmental exposure and pressure makes it ideal for use in gardens, lawns, and agricultural fields. The pipe’s durability ensures that it can handle the demands of irrigation systems, including varying flow rates and pressures.
HVAC and Ventilation Systems
In HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, the 4-Inch PVC Pipe is utilized for ductwork and ventilation applications. It helps direct air flow through the system, maintaining proper air pressure and reducing noise. The pipe’s strength and resistance to corrosion are crucial for ensuring the efficiency and longevity of HVAC systems.
4. Installation and Maintenance
Installation Process
Installing a 4-Inch PVC Pipe involves several key steps:
- Preparation: Clean the pipe ends and fittings thoroughly to remove any debris. Ensure the pipe is cut squarely to achieve a proper fit.
- Application of PVC Primer and Cement: Apply PVC primer to the outside of the pipe and the inside of the fitting to prepare the surfaces for bonding. Follow with a coat of PVC cement on the same areas.
- Joining: Insert the pipe into the fitting, ensuring it is pushed in as far as it will go. Hold the pipe and fitting together for a few seconds to allow the cement to set.
- Curing Time: Allow the joint to cure for the recommended time before applying pressure or stress to the system.
Maintenance Tips
PVC-pipes generally require minimal maintenance. Regular inspections should be performed to check for any signs of damage, such as cracks or leaks. If issues are detected, prompt repairs or replacements should be made. Additionally, avoid exposing PVC pipes to extreme temperatures or harsh chemicals that could affect their performance.
5. Advantages of PVC Pipes
Cost Efficiency
PVC-pipes are known for their cost-effectiveness compared to metal or composite alternatives. Their low initial cost, combined with their durability and low maintenance requirements, makes them an economical choice for various applications. The long-term value provided by PVC pipes is enhanced by their strength and ease of installation.
Corrosion Resistance
One of the primary advantages of PVC-pipes is their resistance to corrosion and rust. Unlike metal pipes, PVC does not degrade when exposed to moisture or chemicals, ensuring a longer service life and reduced maintenance needs. This resistance makes PVC pipes particularly suitable for applications with frequent water or chemical exposure.
Lightweight and Easy Handling
PVC-pipes are significantly lighter than metal pipes, making them easier to handle, transport, and install. This lightweight characteristic simplifies the installation process, reduces labor costs, and minimizes the risk of injury during handling.
6. Comparison with Other Pipe Materials
PVC vs. Metal Pipes
Metal pipes, such as those made from brass or steel, offer high strength but are more prone to corrosion and generally more expensive. PVC pipes, including the 4-inch model, provide a cost-effective, corrosion-resistant alternative with adequate strength for many applications. The lightweight nature of PVC also makes it easier to install compared to metal pipes.
PVC vs. CPVC Pipes
Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC) pipes are designed for higher temperature applications and offer improved thermal resistance compared to standard PVC pipes. While CPVC pipes can handle higher temperatures, PVC pipes are typically more economical and suitable for standard temperature applications, making them a preferred choice for many projects.
7. Safety and Compliance
Safety Guidelines
When working with PVC pipes, it is essential to use appropriate safety gear, such as gloves and safety glasses, to protect against sharp edges and potential chemical exposure during installation. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for safe handling and installation practices to ensure a secure and effective installation process.
Regulatory Compliance
The 4-Inch PVC Pipe complies with industry standards and regulations, including ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) specifications. This compliance ensures that the pipe meets quality and performance standards for its intended applications, providing assurance that it adheres to established guidelines.
8. Conclusion
The 4-Inch PVC Pipe is a versatile and reliable component for various systems, including plumbing, irrigation, and HVAC. Its durable construction, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness make it a valuable choice for many applications. By understanding its specifications, advantages, and maintenance requirements, users can ensure optimal performance and longevity of their piping systems.







































Reviews
There are no reviews yet.