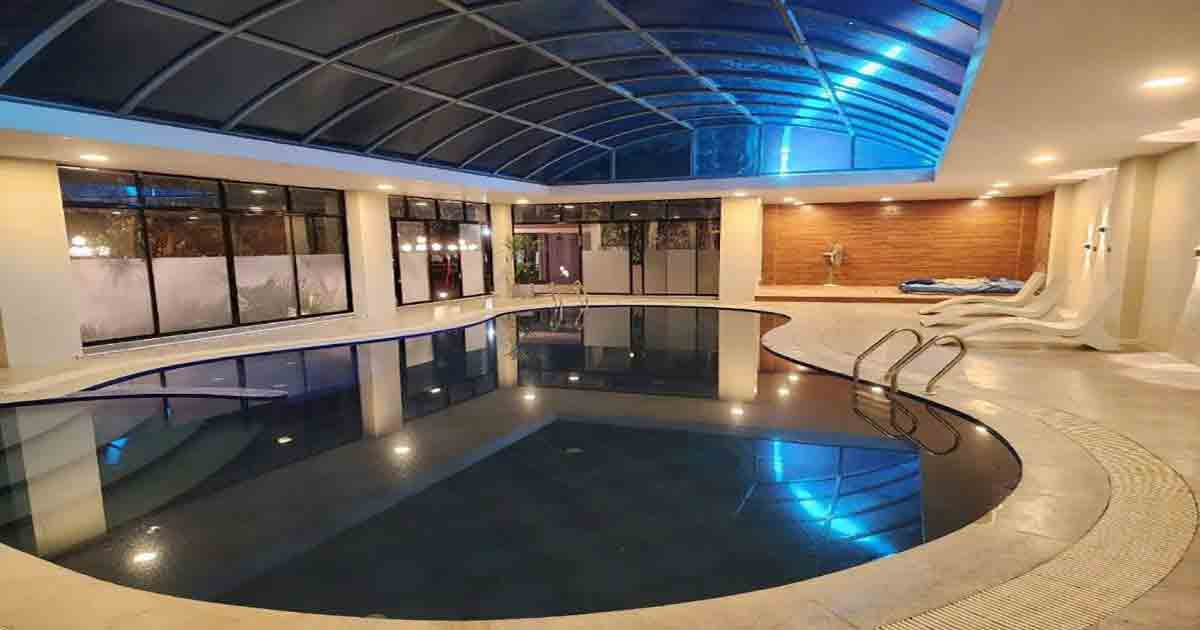
Swimming pool construction details
Swimming pool construction involves a detailed and meticulous process that integrates engineering principles, architectural design, material selection, and skilled craftsmanship to create a functional and aesthetically pleasing aquatic facility. Whether for residential, commercial, or institutional purposes, understanding the intricate details of pool construction is essential for ensuring quality, durability, and compliance with safety standards. This comprehensive guide explores the key elements and construction details involved in building a swimming pool, from initial planning to final finishing touches.
1. Initial Planning and Site Preparation (Swimming pool construction details)
The construction of a swimming pool begins with thorough planning and site preparation to establish a solid foundation for the project. Key considerations during this phase include:
- Site Evaluation: Assessment of the property layout, topography, soil conditions, and existing utilities to determine the optimal location and size of the pool.
- Design Consultation: Collaboration between clients, architects, and pool designers to discuss design preferences, functional requirements, and budget constraints.
- Permitting and Regulations: Obtaining necessary permits and approvals from local authorities to ensure compliance with building codes, zoning regulations, and safety standards.
Keyword: swimming pool construction details
2. Design and Engineering Considerations (Swimming pool construction details)
Once the initial planning phase is complete, pool designers and engineers translate conceptual ideas into detailed designs that prioritize structural integrity, functionality, and aesthetic appeal. Design considerations include:
- Pool Shape and Size: Selection of pool shapes (e.g., rectangular, freeform, geometric) and dimensions based on space availability, intended use, and architectural compatibility.
- Structural Components: Specification of materials for the pool shell, walls, and foundation (e.g., reinforced concrete, steel panels, fiberglass) to ensure durability and stability.
- Hydraulic Systems: Design of plumbing infrastructure, circulation systems, and filtration equipment to maintain water quality and circulation efficiency.
- Safety Features: Integration of safety measures such as fencing, safety covers, and non-slip surfaces to enhance user safety and compliance with regulations.
Keyword: swimming pool construction
3. Excavation and Site Grading (Swimming pool construction details)
Excavation marks the beginning of physical construction, involving the removal of soil and earth to create the pool’s foundation and shape. Key aspects of excavation include:
- Marking and Layout: Marking out the pool perimeter and layout using surveying tools and equipment to ensure precise dimensions and alignment.
- Earthmoving Equipment: Deployment of excavators, bulldozers, and dump trucks to excavate soil, haul debris, and prepare the site for construction activities.
- Soil Stabilization: Implementation of measures to stabilize the excavated area, prevent erosion, and ensure a secure base for the pool structure.
Proper excavation techniques and site grading are essential to achieving the desired pool depth, shape, and dimensions while minimizing disruption to surrounding landscapes.
Keyword: swimming pool construction details
4. Formwork and Reinforcement (Swimming pool construction details)
Once excavation is complete, the next step involves constructing formwork molds and reinforcing the pool structure to support the weight of water and withstand external forces. Details of this phase include:
- Formwork Installation: Setting up temporary molds or frameworks to define the shape and contours of the pool structure before concrete pouring.
- Reinforcement Placement: Installation of steel rebar or reinforcement grids within the formwork to enhance structural strength and prevent cracking.
- Concrete Pouring: Pouring and compacting high-quality concrete mixtures into the formwork molds to create the pool shell, walls, and structural components.
- Curing Process: Allowing sufficient time for concrete curing to achieve optimal strength and durability before proceeding to subsequent construction phases.
Keyword: swimming pool construction details
5. Plumbing and Electrical Installation (Swimming pool construction details)
Efficient plumbing and electrical systems are crucial for maintaining water circulation, filtration, and safety in swimming pools. Detailed aspects of installation include:
- Pipe Layout: Routing PVC or copper pipes to connect pool components such as skimmers, drains, returns, and circulation pumps.
- Filtration Systems: Installation of filtration units (e.g., sand filters, cartridge filters) and circulation pumps to remove debris and maintain water clarity.
- Heating and Ventilation: Integration of pool heaters, heat pumps, or solar heating systems to regulate water temperature and enhance user comfort.
- Electrical Wiring: Installation of underwater lighting, automation controls, safety devices, and grounding systems to ensure electrical safety and operational efficiency.
Keyword: swimming pool construction
6. Surface Finishes and Waterproofing
Surface finishes play a crucial role in enhancing the aesthetic appeal, durability, and waterproofing of swimming pools. Common surface finishes include:
- Plaster: Application of cement-based plaster mixed with additives to achieve a smooth, waterproof surface finish.
- Tiles: Installation of ceramic, glass mosaic, or porcelain tiles to create decorative patterns, enhance durability, and facilitate maintenance.
- Aggregate Finishes: Application of exposed aggregate (e.g., pebble, quartz) to provide texture, slip resistance, and aesthetic variations to the pool surface.
- Vinyl Liners: Custom-fitted vinyl liners stretched over the pool walls and floor to create a seamless, watertight barrier.
Each surface finish option offers unique advantages in terms of aesthetics, maintenance requirements, and longevity, depending on the client’s preferences and budget.
Keyword: swimming pool construction details
7. Decking and Coping Installation
Pool decking and coping materials serve both functional and aesthetic purposes, providing a safe, comfortable area around the pool edge. Details of installation include:
- Material Selection: Choice of materials such as concrete, natural stone (e.g., travertine, slate), pavers, or composite decking based on durability, aesthetics, and maintenance considerations.
- Installation Techniques: Proper installation of decking and coping materials to ensure level alignment, proper drainage, and integration with the pool structure.
- Safety Features: Incorporation of non-slip surfaces, rounded edges, and adequate spacing to enhance safety and prevent accidents around the pool area.
- Design Integration: Coordination of decking and coping designs with surrounding landscapes, architectural features, and outdoor amenities for a cohesive aesthetic appeal.
Keyword: swimming pool construction details
8. Water Features and Enhancements
Incorporating water features enhances the visual appeal and recreational value of swimming pools. Popular water features include:
- Waterfalls and Fountains: Construction of cascading waterfalls, spouts, jets, or laminar flow systems to create soothing water sounds and visual interest.
- Spas and Hot Tubs: Installation of integrated spas or standalone hot tubs with therapeutic jets for relaxation and hydrotherapy benefits.
- Decorative Accents: Addition of decorative tiles, glass accents, underwater LED lighting, or natural rock formations to enhance aesthetic appeal and ambiance.
- Automation and Control: Integration of automation systems for controlling water features, lighting effects, temperature settings, and filtration schedules via mobile devices.
Keyword: swimming pool construction
9. Safety and Compliance
Ensuring safety measures and regulatory compliance is essential in swimming pool construction to protect users and minimize liability risks. Details include:
- Fencing and Barriers: Installation of safety fences, gates, and self-closing latches to restrict access and prevent unsupervised entry into the pool area.
- Safety Covers: Deployment of automatic or manual pool covers to secure the pool surface and prevent accidents, especially in residential settings.
- Underwater Visibility: Placement of underwater lights and clear water conditions for improved visibility of pool bottoms and depths.
- Emergency Equipment: Provision of life-saving equipment (e.g., life rings, safety ropes, first aid kits) and signage to promote safe pool usage and emergency response.
Keyword: swimming pool construction details
10. Final Inspections and Handover
Upon completion of construction, thorough inspections and testing are conducted to ensure compliance with quality standards, safety regulations, and client expectations. Final details include:
- Quality Assurance: Comprehensive checks of structural integrity, plumbing systems, electrical components, and surface finishes to address any deficiencies or adjustments.
- Client Orientation: Orientation sessions and demonstrations for clients on pool operation, maintenance procedures, water chemistry management, and equipment usage.
- Warranty and Support: Provision of warranties for materials, workmanship, and installed equipment, along with ongoing support for post-construction maintenance and service needs.
- Handover Process: Formal handover of the completed pool facility to the client, including documentation, maintenance guidelines, and contact information for future assistance.
Building a swimming pool is a major investment that requires careful planning, design, and execution. Whether you’re constructing a private residential pool or a commercial pool, the process involves multiple phases, from design to the final inspection. In this article, we’ll break down the key details of swimming pool construction, focusing on each phase of the project, the materials used, and considerations that need to be addressed to ensure a successful build.
1. Pre-Construction Planning
Before any digging or construction takes place, thorough planning is essential. During the planning phase, you need to define several key elements of the project:
a. Design and Size
The design phase is critical because it will dictate the overall appearance, functionality, and size of the pool. You’ll need to decide on the shape (rectangular, oval, kidney, or custom design), depth (shallow or deep end), and size (standard lap pool, plunge pool, or larger family pool). Custom-designed pools offer more flexibility but come at a higher cost. A professional pool designer or contractor can assist in turning your ideas into detailed construction plans.
b. Budgeting
Cost estimation is an important part of the pre-construction phase. A rough budget should include not only the construction costs but also the ongoing maintenance, equipment, and any additional features (waterfalls, lighting, pool deck, etc.). Depending on the materials and complexity, residential pool construction costs typically range between $20,000 and $60,000, while commercial pools can exceed $100,000.
c. Site Assessment
A site assessment should be carried out to determine if the ground is suitable for pool construction. The property’s terrain, soil quality, and accessibility for construction equipment can all impact the construction process. You also need to ensure there are no hidden utilities or underground structures that could interfere with excavation.
2. Excavation and Site Preparation
Once the design and site assessment are completed, excavation begins. Excavation is one of the most important and labor-intensive steps in pool construction. Here’s what to expect:
a. Marking the Pool Area
The exact location of the pool is marked using stakes or spray paint. The layout should include the pool shape, location of the pool equipment, and any other features like spa areas or waterfalls.
b. Excavation
Using heavy machinery like backhoes or excavators, workers dig out the pool shape and depth. This process can take anywhere from a few days to several weeks depending on the size and complexity of the pool. The depth varies depending on the pool’s design and intended use (shallow for children, deeper for diving or swimming laps). Excavation can sometimes uncover rocks, tree roots, or other underground materials, which may require additional work and costs.
c. Grading and Drainage
After excavation, the area is leveled and graded to ensure proper water drainage. Proper drainage is crucial to prevent water from accumulating around the pool, which could lead to structural damage. A well-graded base ensures that the pool shell or liner sits perfectly and that water flows away from the pool.
3. Construction of Pool Shell or Structure
With the excavation complete, the actual pool structure is built. There are three primary types of pool construction, each with its own unique process:
a. Concrete Pools (Gunite or Shotcrete)
Concrete pools are the most customizable but also the most labor-intensive and expensive to construct. The process involves creating a steel frame and pouring a thick layer of concrete, either using gunite (sprayed-on concrete) or shotcrete (a high-pressure form of concrete application).
- Steel Reinforcement: The pool’s steel framework is reinforced with rebar or mesh to provide stability and durability.
- Concrete Application: The concrete is then applied over the steel frame. Gunite or shotcrete is sprayed onto the framework, and it hardens to form the pool shell.
- Finishing: After the concrete has set, the pool’s surface is smoothed and finished with plaster, tile, or pebble aggregate. Plaster is the most common finish, but tiles can add a luxury look.
b. Fiberglass Pools
Fiberglass pools are pre-formed shells made from fiberglass and resin. They are delivered to the site in one large piece and lowered into the excavation site. The advantages of fiberglass pools are the shorter construction time, minimal excavation, and lower costs. However, they offer fewer design options compared to concrete pools.
- Installation: The pre-formed fiberglass shell is placed in the excavated hole.
- Backfilling: After the shell is secured, the area around the pool is backfilled with gravel or sand to ensure stability.
c. Vinyl Liner Pools
Vinyl liner pools are made from a steel or polymer frame covered by a custom-made vinyl liner. These pools are less expensive to build but may require liner replacement every 7-10 years.
- Frame Assembly: The frame is assembled and installed into the excavated area.
- Liner Installation: Once the frame is in place, the vinyl liner is stretched over the structure and secured. The liner serves as both the waterproof barrier and the finish.
4. Plumbing, Electrical, and Filtration Systems
After the pool structure is built, the next step involves the installation of plumbing and electrical systems.
a. Plumbing System
The pool’s plumbing system is responsible for water circulation, filtration, and heating. It involves installing pipes for the water intake (skimmers, main drains), water return (jets), and a filtration system. A properly designed plumbing system is essential for maintaining water quality and ensuring that the pool operates efficiently.
Conclusion
Swimming pool construction details encompass a range of technical, aesthetic, and functional considerations that contribute to the successful realization of a pool project. From initial planning and excavation to structural reinforcement, plumbing installation, surface finishes, and safety features, each detail plays a crucial role in creating a safe, durable, and visually appealing aquatic environment.